Imagine you own a well-known and respected restaurant in a bustling city.
Over the years, you’ve built a stellar reputation for serving delicious food, providing excellent service, and creating memorable dining experiences.
As a result, your restaurant enjoys a steady stream of loyal customers, positive word-of-mouth referrals, and glowing reviews.
In the digital marketing realm, having a positive sender reputation is like being that reputable restaurant.
Just as diners are loyal and look forward to frequenting your establishment, recipients trust and eagerly anticipate receiving emails from a company with a positive sender reputation.
Today, we’re going to discuss how you can mitigate hard bounce emails and ensure you maintain a high sender reputation for improved email deliverability. We’ll also discuss:
- How email service providers determine your sender reputation
- The benefits of implementing email authentication protocols
- Anti-spam guidelines and regulations that you should abide by to ensure you never end up in the dreaded spam folder
Without further ado, let’s delve straight into the ultimate guide to mitigating hard bounce emails and recovering your sender reputation.
1 – How to Mitigate Hard Bounce Emails
“By failing to prepare, you are preparing to fail.”
— Benjamin Franklin
Although a hard bounce is defined as a phenomenon that occurs when an email is permanently rejected and cannot be delivered to the recipient, it’s not an occurrence that can’t be negated once it occurs.
There are several best practices that you can implement into your email marketing strategy to reduce hard bounces and improve email deliverability rates, including:
Maintain a Clean and Updated Email List
By ensuring that your list remains squeaky clean (updating and removing invalid or inactive addresses), you can improve email deliverability, reduce email bounce rates, and maintain a high-quality subscriber base.
Most email service providers make this extremely easy by providing bounce reports that categorize emails as either hard bounces or soft bounces.
Regularly review these bounce reports to identify email addresses that consistently result in hard bounces.
It’s important to distinguish soft bounces, which can occur due to temporary issues, from persistent hard bounces.
For instance, if you notice that a specific email address consistently generates three consecutive hard bounces over multiple campaigns, it’s a strong indicator that the email address is invalid or inactive.
Promptly remove such addresses from your mailing list to maintain its cleanliness.
To ensure that the email addresses provided by your customers are valid from the get-go, implement a double opt-in authentication.
Double opt-in is a two-step authentication process where subscribers need to confirm their email address by clicking on a verification link sent to their inbox.
When someone signs up for your newsletter or service, they are sent an automated email with a verification link.
Only when they click on the link and confirm their subscription should their email address be added to your mailing list. This helps ensure that only engaged and valid email addresses are included.
Key Takeaway: Maintaining a clean and updated email list is crucial for better email deliverability. Regularly remove invalid or inactive addresses identified through bounce reports, and implement double opt-in authentication to ensure engaged and valid subscribers.
Implement Email Authentication Protocols
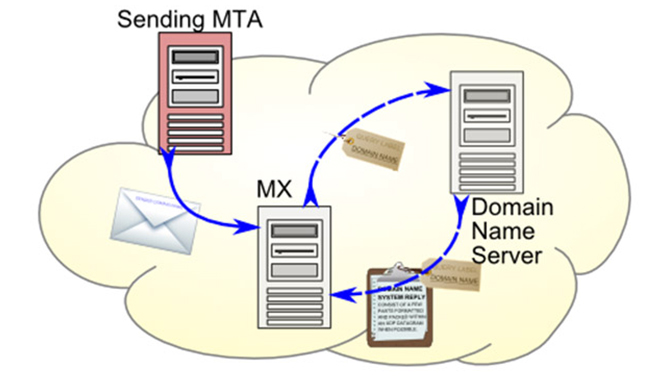
Email authentication protocols, such as Sender Policy Framework (SPF), DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKM), and Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC), are designed to enhance email security by verifying the authenticity and integrity of email messages.
These protocols are checked by email service providers (ESPs) to verify the authenticity of your sender domain. This prevents unauthorized, malicious parties from sending emails that appear to be from your domain.
To further your understanding of email authentication protocols, the following table compares SPF, DKIM, and DMARC, highlighting their primary functions and how they can help reduce hard bounce rates in your email marketing efforts.
| Protocol | Primary Function | How It Reduces Hard Bounce Rates |
| SPF | Verifies that the sender IP is authorized by the domain owner | By verifying the sender, it reduces the chance of emails being rejected or marked as spam |
| DKIM | Attaches a digital signature to the email, verifying it hasn’t been tampered with during transit | The digital signature increases the authenticity and integrity of your emails, reducing the probability of them being marked as spam |
| DMARC | Builds upon SPF and DKIM and allows the sender to indicate that their emails are protected by these protocols | Ensures that the recipient server can trust the source of the email, thus decreasing the likelihood of rejection and hard bounces |
To illustrate, let’s say you run email marketing campaigns for an online banking service. By implementing email authentication protocols, you ensure that only legitimate emails sent from your official domain are recognized as authentic.
This prevents cybercriminals from sending fraudulent emails to your customers while pretending to be your bank, and attempting to steal sensitive information.
Implementing email authentication protocols demonstrates your commitment to email security and will protect your customers from email-based threats. This, in turn, fosters trust and confidence in your brand.
Comply With Anti-Spam Guidelines and Regulations
While most ESPs have their own specific anti-spam guidelines and regulations, there are a few overarching industry standards that all identify with. Some of these include:
- Controlling the Assault of Non-Solicited Pornography And Marketing Act (CAN-SPAM USA)
- Canada Anti-Spam Legislation (CASL)
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR European Union)
Familiarize yourself with these guidelines according to the country you’re from as they’re usually the primary base used by ESPs to develop their individual policies.
They may provide guidance on how to comply with said policies and offer features or tools that may help you escape common anti-spam pitfalls.
For example, the CAN-SPAM Act is a United States federal law that sets the rules for commercial email communication.
It requires you to include specific information in your commercial emails, such as a valid physical postal address and a clear opt-out mechanism.
By complying with the CAN-SPAM Act, you ensure that your email communications are transparent and that recipients have the ability to opt out of receiving future emails.
ESPs often provide guidance on how to comply with the CAN-SPAM Act, including features or tools to help you include the required information and manage opt-out requests effectively.
For instance, Gmail put together an actionable and comprehensive guide based on CAN-SPAM Act guidelines that can help you prevent your emails from being blocked and sent to spam.
Top Tip: Familiarizing yourself with anti-spam guidelines, such as CAN-SPAM, CASL, and GDPR, is important—they serve as the foundation for ESPs’ individual policies and provide guidance to prevent common anti-spam issues.
2 – How to Recover Your Sender Reputation
Picture the following scenario: You’re a delivery driver working for a reputable fresh goods company.
Due to some careless mistakes and poor driving habits, you’ve received numerous customer complaints about late deliveries, damaged packages, and rude behavior.
As a result, your reputation as a delivery driver becomes tarnished. In this scenario, your sender reputation is similar to your reputation as a delivery driver.
Just as customers rely on you to deliver packages promptly and with care, email recipients expect legitimate, relevant, and valuable emails in their inboxes.
If you consistently send emails that are irrelevant, misleading, or show up as bounce messages, it’s like delivering packages late, damaged, or to the wrong address.
Over time, this negative experience leads to recipients flagging your emails as spam, unsubscribing, or complaining to email providers, negatively affecting your sender reputation.
As a consequence, your future emails are more likely to be treated as suspicious or filtered out altogether by ESPs.
All hope is not lost.
Just as a delivery driver with a poor reputation must take steps to improve their behavior and regain customer trust, a sender with a poor reputation needs to address the issues causing complaints and take proactive measures to restore their reputation.
First things first, you have to understand how your sender reputation is decided by mailbox providers and check your sender reputation score on a trusted website in order to understand how deep the damage runs.
Let’s break the whole process down into three actionable and digestible steps that you can apply to help you with email bounce handling:
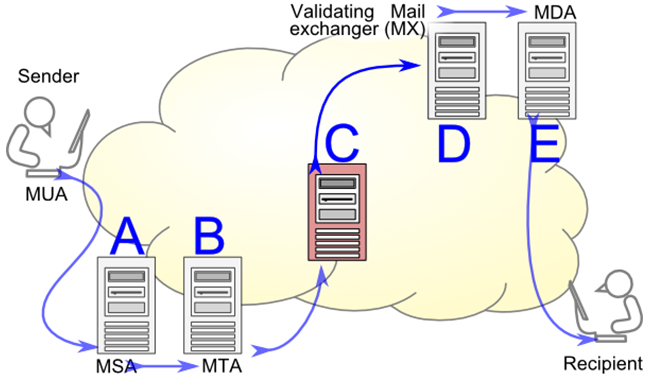
Step 1 – Understand the Importance of Checking Sender Reputation
Checking your sender reputation helps you assess the health of your email deliverability and identify potential issues that may be affecting your email campaigns.
ESPs check your domain or IP address every time you try to send their recipients an email to see how subscribers are interacting with your messages. This will determine your sender reputation.
Then, they use a unique algorithm to give you a reputation score. Usually, they group you in one of three categories including:
- Poor (0–70): This is the worst possible score your domain can have, and you will need to take immediate action to repair your sender reputation.
Falling into this category can reduce your email deliverability, decrease your engagement rates, and increase your likelihood of being placed on email blacklists. - Fair (70–80): Your sender reputation is average, but there’s room for improvement. ESPs will be watching you like a hawk and may even flag legitimate emails, harming your deliverability.
- Good (80–100): This is every email marketer’s dream. ESPs trust and recognize your domain as a trusted, reputable source and don’t scrutinize your emails as much. You experience high email deliverability and enhanced brand reputation and credibility.
The table below provides a concise comparison of how different email service providers (ESPs) use unique reputation systems and the potential impact these systems have on email deliverability.
| Email Service Provider | Unique Reputation Scoring System | How It Affects Email Deliverability |
| Gmail | Uses machine learning, user interaction | Directly affects placement in inbox or spam |
| Yahoo Mail | Uses a mix of hard bounces, spam complaints | Impacts deliverability rate |
| Outlook.com | Utilizes user feedback, content filtering | Impacts whether email lands in inbox or junk |
Step 2 – Utilize Sender Reputation Monitoring Tools
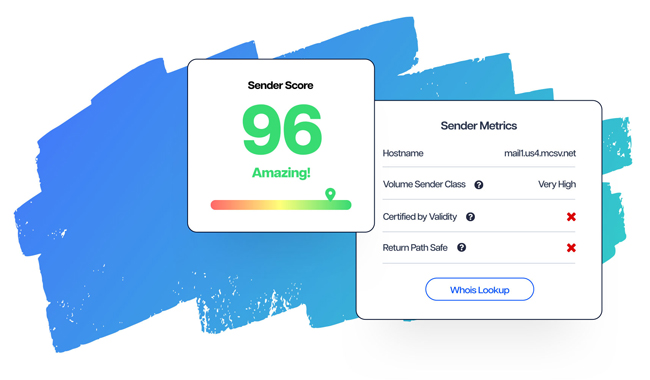
There are various reputable sender reputation monitoring tools, such as Sender Score, that you can utilize to gain valuable insights into your sender reputation.
These platforms have established their credibility in the industry and offer reliable assessment mechanisms for evaluating your email practices.
To illustrate, let’s imagine you’ve been running an email campaign that experiences a sudden surge in complaint rates, a drop in email deliverability, and a decline in engagement metrics.
You suspect that your domain has either been blacklisted or that most of your emails are landing in the spam folder. However, to determine the real cause of the problem, you use Sender Score to check where the problem arises.
Sender Score then runs a series of tests on your domain to assess various factors that contribute to your sender reputation, including email volume, complaint rates, blacklisting status, and spam trap hits.
This generates a report that confirms your domain is listed on a popular blacklist and detects a spike in complaint rates that is causing your emails to land in spam.
Armed with this information, you promptly investigate the reason for the blacklisting, resolve any underlying issues, and take the necessary steps to get delisted.
Additionally, you refine your email content, implement your email segmentation strategies, or improve list hygiene to increase engagement and enhance your sender reputation.
“A small list that wants exactly what you’re offering is better than a bigger list that isn’t committed.”
— Ramsay Leimenstoll
Step 3 – Make a Habit of Regularly Checking Your Sender Reputation
“Marketers need to build digital relationships and reputation before closing a sale.”
— Chris Brogan
Establish a routine where you clean and update your email list while also checking your sender reputation every month. This allows you to regularly monitor your sender reputation and track changes and trends in your reputation metrics.
It further enables you to identify any gradual declines or sudden spikes in reputation that may require attention. Early detection of such problems allows you to address them promptly, preventing further damage to your sender reputation.
Addressing any issues identified through reputation monitoring helps you resolve them before they escalate and impact your email deliverability.
For example, if you notice a sudden increase in spam complaints, you can investigate the cause and take corrective measures, such as refining your email content or reconfirming subscriber consent.
Fun Fact: Did you know that the term “spam” for unsolicited email originated from a Monty Python sketch about canned meat in 1970?
Make Your Sender Reputation Bulletproof From Hard Bounce
While hard bounce emails are a marketer’s worst nightmare, they’re not the be-all and end-all.
You can mitigate the effects of hard bounces by maintaining a clean email list, verifying email addresses, and using authentication protocols like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC.
Moreover, by understanding how email service providers designate sender reputation, you’ll be able to identify the root of the problem and effectively work towards solving it.
At OnDigitalMarketing, we provide tactical and real-world education that drove $350 million for clients in revenue last year alone.
Our methods have been tried and tested across 212 countries after undergoing intense peer review from third-party industry experts.
Join our newsletter today to receive exclusive insider tips. Plus, be the first to know about collaborations with partner websites, and fresh tips and “how-to’s” on all things digital marketing.

